5 Key Motifs in Islamic Art Decor

Islamic art is renowned for its rich aesthetic and complex motifs, which serve as more than mere decorations; they are a reflection of the Islamic ethos, identity, and spiritual dimensions. In this extensive exploration, we delve into five pivotal motifs found in Islamic art that encapsulate the cultural, spiritual, and artistic nuances of this vast tradition. Let's embark on a journey through the labyrinth of Islamic artistic expressions, where form meets function in a symphony of beauty and devotion.
The Arabesque: Nature as an Echo of the Divine

The arabesque is perhaps one of the most recognized motifs in Islamic art, characterized by intricate, flowing patterns that resemble foliage and other natural elements. These patterns:
- Symbolize the infinite nature of the Divine Creator.
- Serve as a visual reminder of the beauty and unity found in nature.
- Often intertwine to form borders or standalone designs.
📝 Note: Arabesque patterns often avoid representing life forms directly, adhering to the Islamic aversion to idol worship, instead, focusing on abstraction and stylized elements of the natural world.
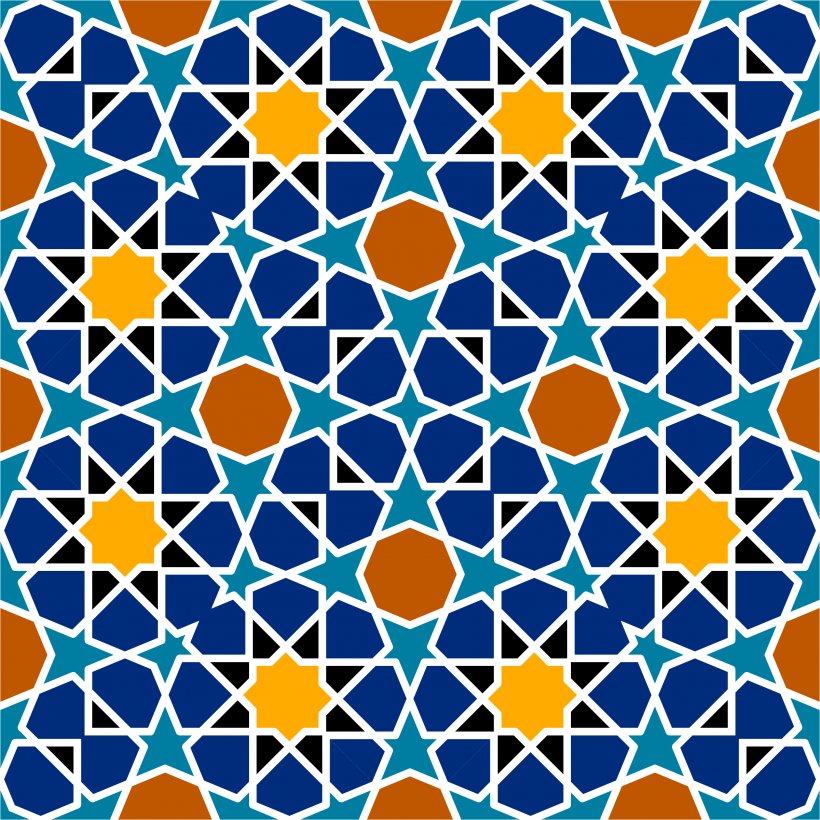
Geometric Patterns: The Language of Infinity

Geometric patterns in Islamic art are a testament to:
- The human quest for understanding the underlying structure of the universe.
- The concept of infinity, where lines, curves, and polygons interlock in endless, harmonious ways.
- The mathematical precision inherent in Islamic philosophy and science.
| Common Elements in Geometric Patterns | Significance |
|---|---|
| Circles | Unity and perfection |
| Star polygons | The Divine Light |
| Interlocking patterns | Continuity of life and eternity |

Calligraphy: The Art of the Written Word
Calligraphy holds a special place in Islamic art, serving as a conduit for the Word of God from the Holy Quran. Here’s what makes it significant:
- Transforms writing into a visual art form.
- Can be both functional (i.e., for Quranic verses) and decorative.
- Emphasizes the importance of text and the divine through aesthetic beauty.
📝 Note: Different regions of the Islamic world have developed unique styles of calligraphy, from the elegant Kufic to the flowing Nastaliq, each telling a story of regional identity.
The Alhambra: A Symphony of Islamic Art

The Alhambra, nestled in Granada, Spain, is a masterpiece where various Islamic motifs culminate to create an unparalleled architectural spectacle. Here:
- Arabesque patterns adorn walls, floors, and ceilings.
- Intricate geometric designs interlace with flowing water features.
- Calligraphic inscriptions elevate every corner with verses of poetry and Quran.
This site not only reflects artistic excellence but also embodies a philosophy of beauty, symmetry, and harmony.
The Lotus and Peony: Symbolism in Architecture

Moving beyond the common motifs, symbolism through floral elements like the lotus and peony have been incorporated into Islamic architecture, particularly in:
- India, where the lotus represents purity and creation.
- Chinese-influenced regions, where the peony signifies prosperity and nobility.
These symbols, while not exclusively Islamic, find resonance with Islamic themes of spiritual growth and divine perfection.
Summarizing the intricate tapestry of Islamic art, we've explored how motifs like arabesque, geometric patterns, calligraphy, and architectural masterpieces like the Alhambra, along with the symbolic integration of floral elements, weave together to form an artistic tradition that transcends mere aesthetics. These motifs are not just about creating visual harmony; they embody profound philosophical, spiritual, and cultural ideas that have influenced countless generations and continue to inspire global appreciation for Islamic artistic legacy.
What is the significance of geometric patterns in Islamic art?

+
Geometric patterns in Islamic art signify the infinite nature of God, the harmony of the universe, and the underlying mathematical order present in creation. They emphasize the concept of interconnectedness and the eternal.
Why are figurative representations rare in Islamic art?

+
Islamic art often avoids figurative imagery due to the prohibition of idolatry in Islam. The focus shifts to abstraction, allowing for an appreciation of God’s creation through non-representational forms.
How does Islamic calligraphy differ from other forms of writing?

+
Islamic calligraphy transforms writing into an art form, with each style expressing regional cultural nuances. It’s not just about legibility but also the spiritual and aesthetic dimensions of the text, particularly when inscribing verses from the Quran.
What role does water play in Islamic architecture?

+
Water in Islamic architecture is often used in fountains, pools, and gardens, symbolizing paradise and purification. It creates a soothing environment conducive to contemplation and prayer.
Are there influences from other cultures in Islamic art?

+
Absolutely, Islamic art has assimilated influences from cultures it encountered through trade, conquest, or cultural exchange, incorporating elements like floral motifs from Chinese art or geometric patterns inspired by Byzantine mosaics.



